ISOSTASY AND GRAVITY CORRECTIONS
Isostasy is the gravitational equilibrium between earth’s crust and mantle
gravitational balance
AIRY’S THEORY
Equal density and unequal thickness
It is based on root and anti-root theory
Root : in case of high elevation (mountain)
Anti-root : in case of low elevation (ocean)
Root = ρch/(ρm-ρc)
Anti-root = (ρc-ρw)z / (ρm-ρc)
h= height of mountain
z = depth of ocean
PRATT’S THEORY
Unequal density at uniform depth
Not based on root and anti-root
ρ = ρcD/(D+h)
ρ' = (ρcD - ρwZ)/(D-z)
D= thickness of crust
z=depth of ocean
VENING MEINESZ
The upper layer behaves like an elastic plate overlying a weak fluid.
It accounts for regional isostatic compensation
Depends on elastic properties of the lithosphere
Local compensation : Airy’s and Pratt’s theory
Regional compensation : Vening meinesz theory
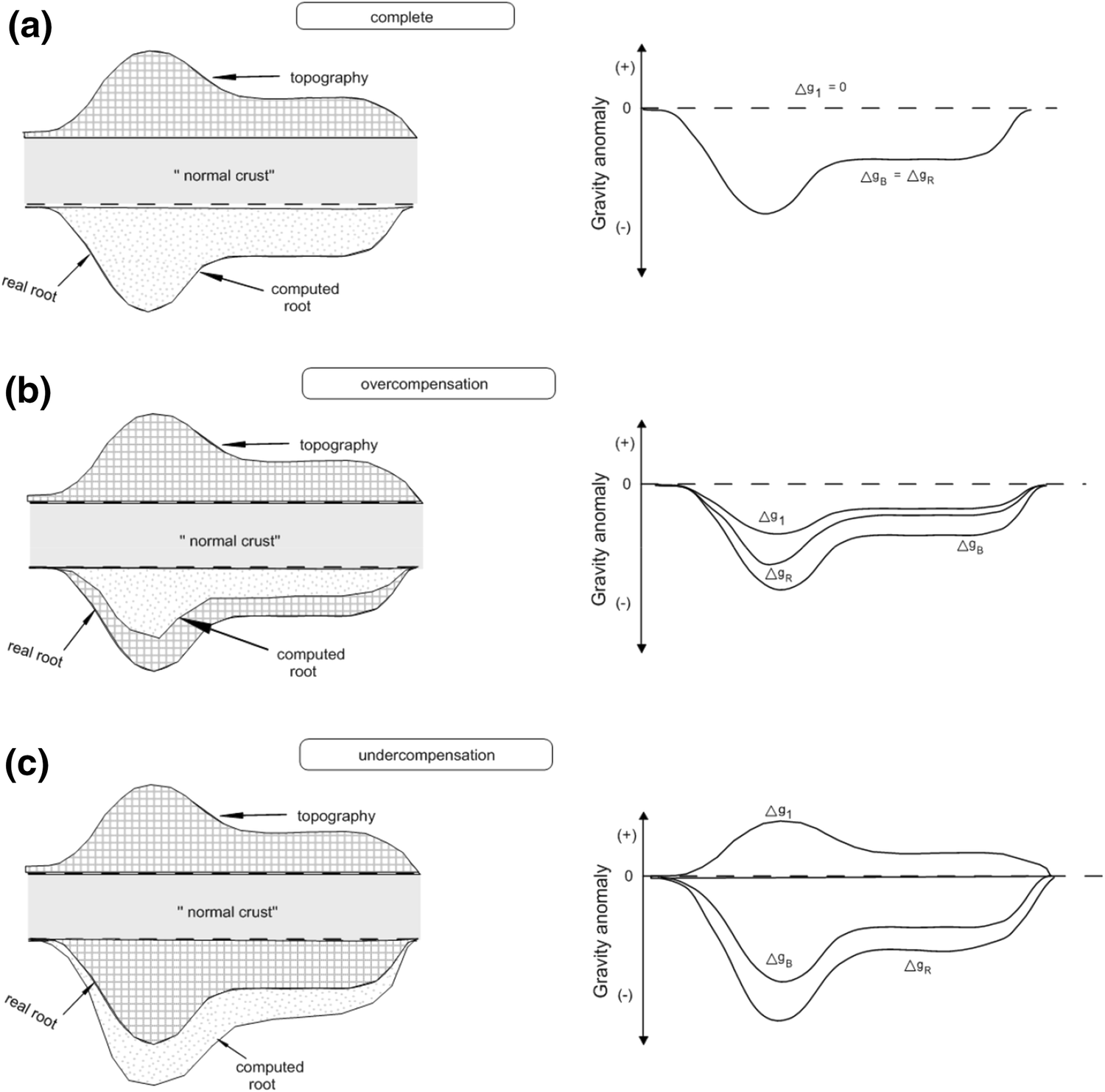
ISOSTATIC COMPENSATION
Gravity anamoly = (observed - calculated) gravity value
Isostatic gravity anamoly = Bouguer anamoly - Computed anamoly of root zone
1) OVERCOMPENSATION
Occurs when a land-high is reduced (as by erosion)
Root of overcompensated landmass will readjust and shift upward w.r.t root zone
Computed root is smaller than real root
Isostatic gravity anamoly is negative
Bouguer anamoly is also negative
2) FULL COMPENSATION
Computed root is in hydrostatic equilibrium with its root zone
Bouguer anamoly and Computed anamoly are equal in magnitude but opposite sign
Isostatic gravity anamoly will be zero (as opposite in algebraic sign giving zero-value)
Bouguer anamoly is negative
3) UNDERCOMPENSATION
Computed root is larger than real root
Isostatic gravity anamoly is positive
Bouguer anamoly is negative
GRAVITY CORRECTIONS
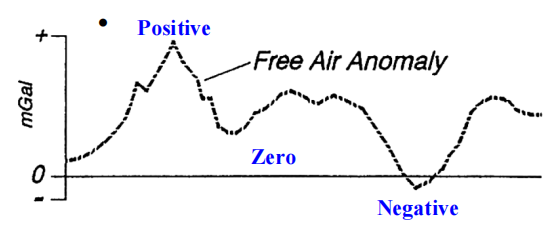
1) FREE AIR CORRECTION
Corrects for the change in gravity due to change in the height
Positive : if station is above sea level
Negative : if station is below sea level
FAC = 0.3086h mgal (when h is in meter)
Free air anamoly = g0 - gλ + 0.3086h
2) BOUGUER CORRECTION
Corrects for the change in gravity due to lateral change in density
Bouguer correction and free air correction act opposite to each other
Positive : if station is below sea level
Negative : if station is above sea level
BC = 2πGρh = 0.0419ρh (h in meter and ρ in gm/cc)
Bouguer anamoly = g0 - gλ + FAC - BC + TC
3) TERRAIN CORRECTION
Terrain correction is always added
Used to nullify the effects of terrain features using ‘Hammer chart’
It tend to lower down the gravity value at a station point
4) LATITUDE CORRECTION
Gravity value increases with latitude i.e from Equator to Pole but decreases with radius
Difference in gravity value = 5186 gals (1 gal= 1cm/s2)
Maximum : At Poles = 9.83 m/s2
Minimum : At Equator = 9.78 m/s2
Gravity value varries 57 mgal with 10 latitude
5) TIDAL CORRECTION
The period of tide correction is known as drift correction
Amplitude variation in g due to tidal effect is 0.3 gal
6) EOTVO’S CORRECTION
Required in Airborne and shipborne gravity survey
Can be made in marine gravity survey and areogravimetry
Comments
Post a Comment