CLASSIFICATION OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
CLASSIFICATION OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
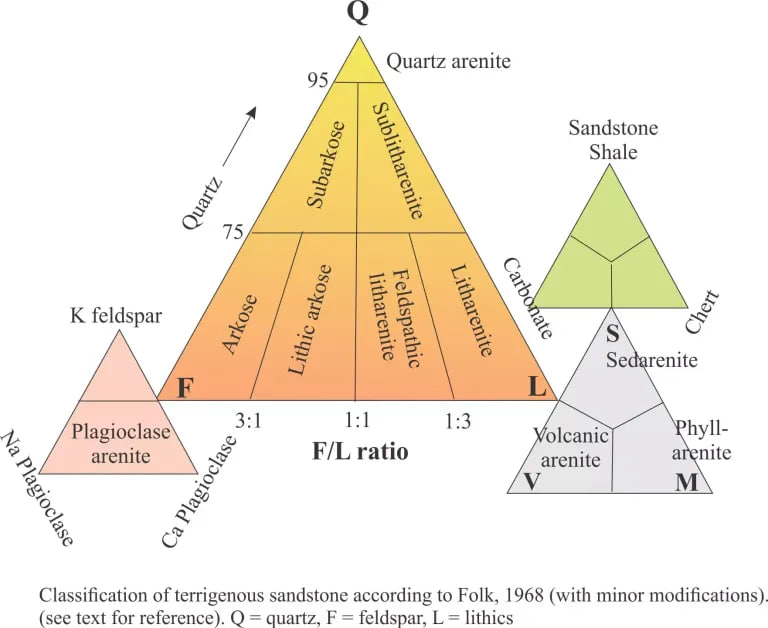
SANDSTONE CLASSIFICATION
Arenite < 15% matrix
Wacke > 15% matrix
Mudstone > 75% matrix
Arkose > 25% feldspar
Quartz arenite > 95% quartz
BASED ON MATURITY
Quartz wacke : Mineralogically mature but texturally immature
Quartz arenite : Both mineralogically and texturally mature
Feldspathic wacke : Both mineralogically and texturally immature
CONGLOMERATE CLASSIFICATION
Conglomerates are rounded grains belongs to Rudaceous rocks
Oligomict : Clasts are of single rock type
Polymict : Clasts are of different rock type
Diamict : Matrix % is high (Clasts are completely surrounded by matrix)
Petromict : Unstable or metastable clasts
OTHER TERMS
Agglomerate : volcanic origin
Fanglomerate : found in case of alluvial fan
DUNHAM’S CLASSIFICATION
MUD SUPPORTED
Mudstone < 10 % grain
Wackestone > 10% grain
GRAIN SUPPORTED
Grainstone < 10% grain
Packstone > 10 % grain
FOLK CLASSIFICATION
Oolite : Spherical grains with internal structure ( < 2 mm)
Pisolite : Concentric layers without internal structure ( > 2mm)
Cortoids : Rounded grains
Oncoids : Grains containing nucleus surrounded by irregular, non-concentric laminae
Peleods : Small micritic grains without internal structure
HJULSTROM DIAGRAM
The Hjulström Curve shows the linkage between sediment size and the velocity needed to erode, transport or deposit.
The upper line shows the erosional velocity or critical erosion velocity needed to initiate sediment erosion.
The lower line shows the fall or settling velocity
In between the two there is the transportation of sediments.
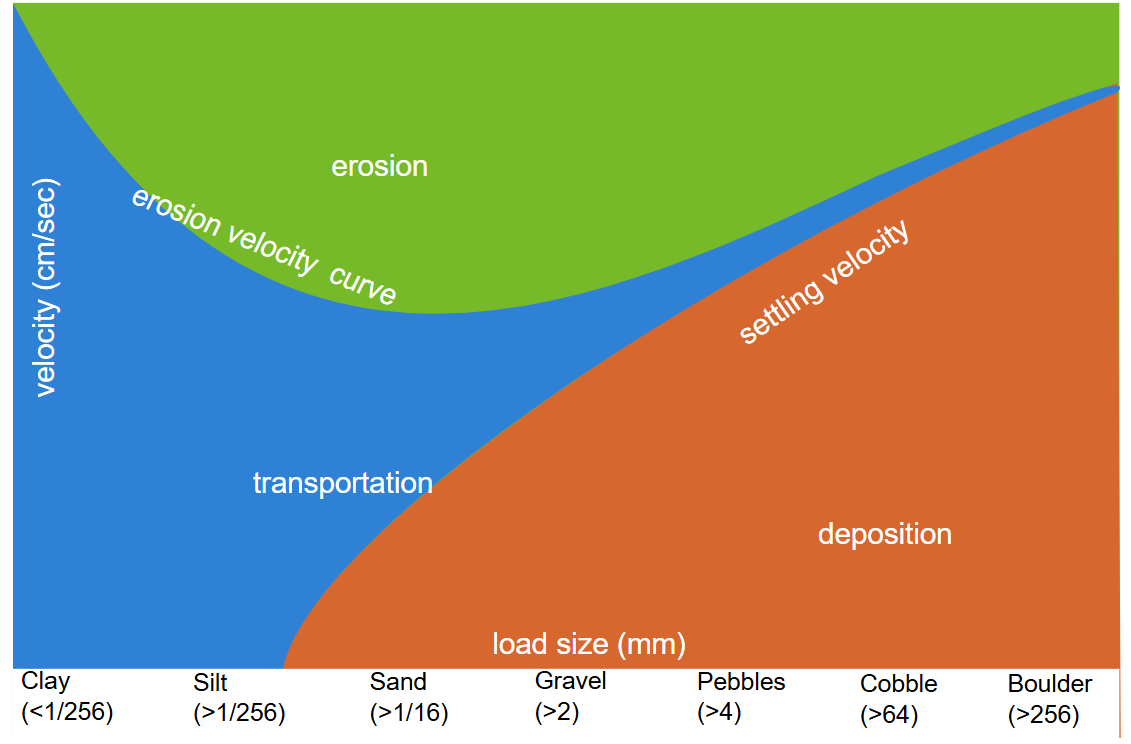
Filip Hjulström’s curve implies that sediments such as sand need low velocities to be dislodged from the bed. This is because sand particles are incohesive; they don’t stick together.
Critical velocity of silt and clay is greater than sand.
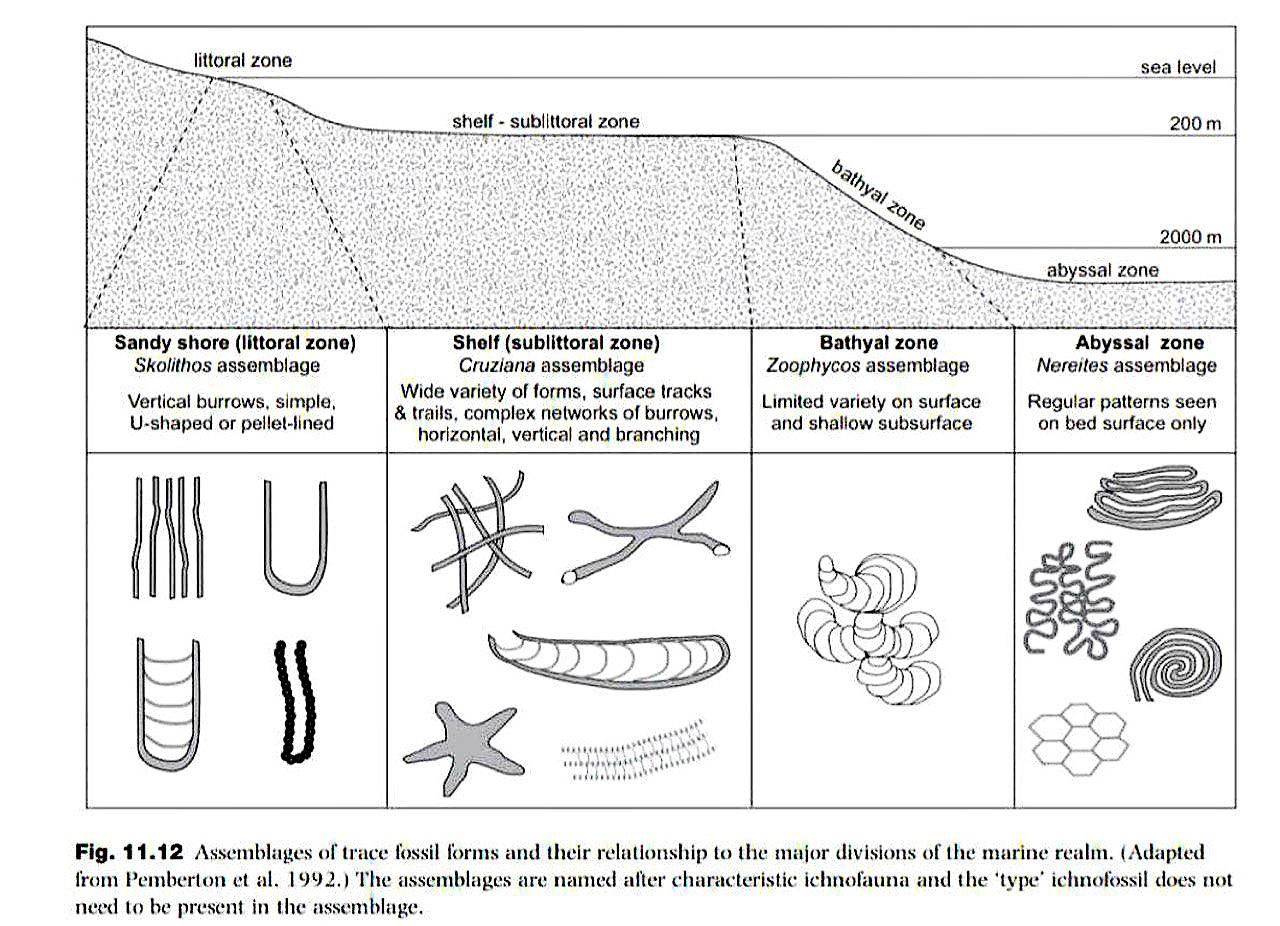
BATHYMETRY
Sequence of increasing depth
Littoral zone : Skolithos
Sublittoral zone : Cruziana
Neritic zone
Bathyal zone : Zoophycus
Abyssal zone : Nereites
Hadal zone
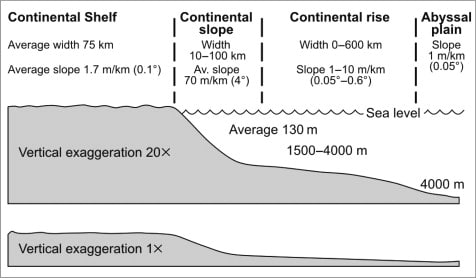
Sequence of inceasing depth
Continental shelf
Continental slope
Continental rise
Abyssal plain
Comments
Post a Comment