BARC EXAM 2024 MEMORY BASED QUESTIONS
1) The radiogenic heat produced by 1 kg of rock is maximum for
a) Granite
b) Gabbro
c) Granodiorite
d) Peridotite
Ans : Radioactive elements are rich in continental crust and their abundance decreases downwards.
The radiogenic heat produced by a rock depends on its content of radioactive elements, primarily uranium (U), thorium (Th), and potassium (K). Among the given options:
- Granite ia a felsic intrusive igneous rock which has composition of Quartz and K-feldspar, K-feldspar is rich is potassium which is a radioactive element.
- Gabbro is a mafic rock with lower concentrations of radioactive elements having composition of Plagioclase and CPX
- Peridotite is ultramafic and has the least amount of radioactive elements mainly rich in Olivine.
Since granite generally has the highest concentration of radioactive elements, it produces the most radiogenic heat.
2) The geoid can be best defined as
a) An oblate spheroid that approximates the shape of earth
b) A surface over which value of gravity is constant
c) Physical surface of earth
d) An equipotential surface of earth
Ans: The geoid is defined as the equipotential surface of Earth's gravity field that always coincide with mean sea level. It is an imaginary surface where the gravitational potential remains constant, meaning that a ball placed on it would not roll due to gravity differences.
3) Which of the following represent the miller indices of octahedron ?
a) {001}
b) {101}
c) {111}
d) {100}
Ans :
OCTAHEDRON(8) : {111}DODECAHEDRON(Rhombic) (12) : {110}
TETRAHEXAHEDRON (24) : {0kl}
TRAPEZOHEDRON (24) : {hll}
TRIS-OCTAHEDRON (24) : {hhl}
HEXA-OCTAHEDRON (48) : {hkl}
4) The line on a map joining places of equal rainfall is called an _____
a) Isotach
b) Isoneph
c) Isohyet
d) Isohel
Ans: Isotach - equal wind speed
Isoneph: equal cloud cover
5) Which of the following phyllum shows unsegmented body?
a) Arthropoda
b) Trilobita
c) Chordata
d) none of the above
Ans :
Arthropoda → Incorrect
Arthropods have a segmented body, typically divided into head, thorax, and abdomen (e.g., insects, crustaceans).
Trilobita → Incorrect Trilobites belong to the phylum Arthropoda and also have a segmented body, divided into cephalon, thorax, and pygidium.
Chordata → Incorrect
Chordates (e.g., vertebrates) may show segmentation in the embryonic stage (like the vertebral column or muscle segments), though not always externally visible.
None → Correct
All the mentioned phyla show segmentation at some stage in their life cycle.
6) What is grouting?
a) A method of applying concrete projected at high velocity primarily on to a vertical or overhead surface
b) Injecting dense fluid that hardens used to fill void, cracks, and joints in concrete structures
c) It is a long anchor bolt used for stabilizing rock excavations, which may be used in tunnels or roadcuts
d) Spraying of concrete at high velocity
Ans : Grouting is specifically the process of injecting a pumpable material (the grout) into voids or cracks. This material then hardens to provide stability, seal against water, or fill gaps.
- Shotcrete : A method of applying concrete projected at high velocity primarily on to a vertical or overhead surface describes shotcrete or gunite
- Rock bolting : It is a long anchor bolt used for stabilizing rock excavations, which may be used in tunnels or roadcuts
7) The maximum and minimum principal stresses are represented by σ1 and σ3 respectively. The differential stress have an absolute value greater than σ1 when ,
a) σ1 and σ3 both are tensile
b) σ1 and σ3 both are compressive
c) σ1 and σ3 both are equal
d) σ1 is compressive and σ3 is tensile
Ans : The differential stress is defined as
Differential Stress = σ1−σ3
For the absolute value of differential stress to be greater than σ1, we require:
∣σ1−σ3∣>σ1|
σ1 is compressive and
- This means σ3 is negative (tensile).
- The differential stress becomes σ1−(σ3)=σ1+∣σ3∣
- Since ∣σ3∣ is positive, this value can exceed σ1
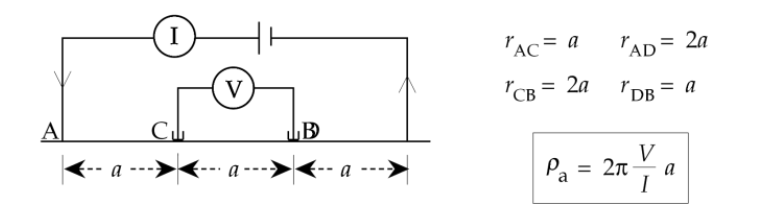
8) Among the four electrode configuration, which of the following is best suited for archeological survey?
a) Schlumberger
b) Pole - Pole
c) Wenner
d) Dipole - Dipole
Ans :
Wenner :
Current and potential electrodes are overlapping with each other
Current and potential electrodes have a common mid-point
difference between adjacent electrodes are equal
used for lateral resistivity variation (Resistivity profiling) i.e shallow subsurface profiling
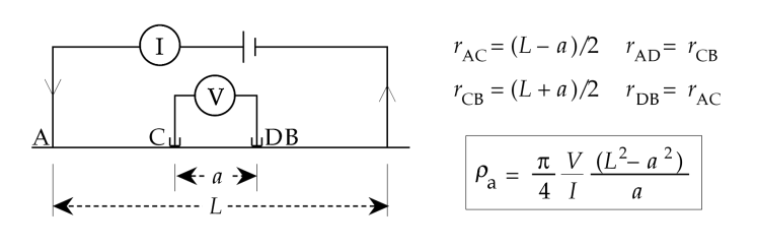
Schlumberger :
Current and potential electrodes are overlapping with each other
Current and potential electrodes have a common mid-point
used for vertical resistivity variation (resistivity sounding) i.e deep subsurface profiling
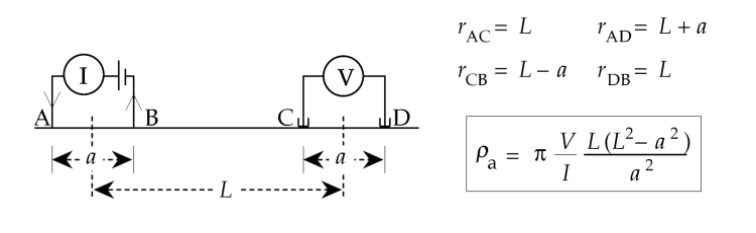
Dipole-Dipole:
Distance b/w two current electrodes are equal
Current and potential electrodes are not overlapping with each other, they got separated
Used in archaeological survey
Pole-Dipole:
One current electrode is at great distance (infinite)
Electrodes are not overlapping with each other
Suitable for moderate depth investigation
Pole-Pole:
9) Which among the following is the peculiarity of Honshu, Japan?
a) Single Benioff zone and volcanic island
b) Double Benioff zone and volcanic island
c) A volcanic island
d) None of the above
Ans : Honshu, the largest island of Japan, is located in a tectonically active region where the Pacific Plate and Philippine Sea Plate subduct beneath the Eurasian Plate and North American Plate. This subduction results in:
- Volcanic activity due to melting of the subducted slab.
- A double Benioff zone (also known as a double seismic zone), where two distinct planes of earthquake activity exist within the subducting slab at different depths.
10) Match group-I with group-II
Ans : P → 3 (Calc-silicate, moderate P-T), Q → 4 (Pelite, high P, low T, R → 2 (Metabasite, low P, high T), S → 1 (Pelite, low P, high T)
Diopside - Tremolite - Fosterite
- Diopside (clinopyroxene) and tremolite (amphibole) are characteristic of calc-silicate rocks.
- Fosterite (olivine) suggests a moderate P-T environment.
Talc - Phengite - Kyanite
- Talc and phengite (mica) indicate low-temperature conditions.
- Kyanite forms under high pressure conditions.
- Found in Blueschist facies
Hornblende - Cummingtonite - Plagioclase
- Hornblende (amphibole) and cummingtonite (another amphibole) are commonly found in metabasites.
- Plagioclase also occurs in amphibolites.
- Low-pressure, high-temperature conditions favor this assemblage.
Andalusite - Cordierite - Biotite
- Andalusite and cordierite are typical of low-pressure, high-temperature conditions in pelitic rocks found in Buchan zone of contact metamorphism
- Biotite is also common in these settings.
11) Which of the following is correct chronological sequence for Iron formations?
a) Algoma > Superior > Rapitan > Minnete
b) Algoma > Superior >Minette > Rapitan
c) Rapitan > Minette > Superior > Algoma
d) Algoma > Minette > Superior > Rapitan
Ans :
Algoma: Archean (Volcanogenic sediments)
Superior : Paleoproterozoic (Stable continental shelf)
Rapitan : Neoproterozoic (Glacial sediments)
Minette : Alternate hematite and qtz
12) Which types of dam requires strong abutments as canyon will bear most of the load?
a) Gravity dam
b) Arch dam
c) Buttress dam
d) Embankment dam
Ans :
13) Telluric currents are generally found in _____ a) Mesosphere
b) Stratosphere
c) Asthenosphere
d) Lithosphere
Ans : The lithosphere, which includes the Earth's crust and uppermost mantle, is where telluric currents primarily occur. These currents interact with conductive materials such as ores and water-rich regions.
14) The upper surface of phreatic zone has a water pressure
a) Greater than atmospheric pressure
b) Equal to atmospheric pressure
c) Smaller than atmospheric pressure
d) Twice of atmospheric pressure
Ans : The phreatic zone, also known as the saturated zone, is the part of an aquifer where all the pore spaces are completely filled with water. The upper surface of the phreatic zone is called the water table. In case of water table the water pressure becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure.
15) In which class of Ramsay classification, the dip isogons diverge downward axial surface?
a) Class I
b) Class IB
c) Class II
d) Class III
Ans :
16) The interlimb angle of open fold is
a) 180 - 120
b) 120 - 70
c) 70 - 30
d) 30 - 10
Ans :
17) Identify the dam in the given figure
a) Gravity dam
b) Arch dam
c) Buttress dam
d) Embankment dam
18) The term Deccan trap was given by
a) Edward suess
b) W.h. sykes
c) H G medlicott
d) Henry Wesley voysey
Ans : The term "Deccan Trap" refers to the extensive basaltic lava flows that cover a large part of western and central India, primarily formed during the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) boundary in 66 Ma.
The term was first introduced by W.H. Sykes in 1833 while describing the layered basaltic formations of the Deccan Plateau. The word "Trap" comes from the Swedish word "Trappa," meaning "stair," referring to the step-like appearance of these lava flows.
The Réunion hotspot (produced the Deccan Traps about 66 million years ago) coincides with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Kerguelen hotspot produced the Rajmahal trap in upper creataceous and it is older than Deccan trap.
19) The lava which is known as ''oldman's skin''
a) Aa lava
b) Pahoehoe lava
c) Composite lava
d) Pillow lava
Ans :
20) The process during earthquakes where soil grains are surrounded by water droplets are known as
a) Soil creep
b) Solifluction
c) Liquefaction
d) Landslide
Ans :
Liquefaction occurs during earthquakes when saturated, loose, granular soil loses its strength and behaves like a liquid due to increased pore water pressure.
This happens because the shaking causes water to surround soil grains, reducing friction and making the ground unable to support structures.
It is common in low-lying coastal areas, riverbanks, and reclaimed land.
21) The zones which are part of supergene enrichment are
a) Zone oxidation and zone of reduction
b) Zone of oxidation and zone of aeration
c) Leached zone and zone of oxidation
d) Zone of sulphidation and zone of reduction
Ans :
22) Iridium anamoly is associated with which boundary
a) Cretaceous - paleogene
b) Permian - Traissic
c) Devonian - Silurian
d) Cambrian - Ordovician
Ans : The term iridium anomaly commonly refers to an unusual abundance of the chemical element iridium in a layer of rock strata at the Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) boundary.
23) Herringbone structure is generally related to which of the following environments?
a) Fluvial
b) Aeolian
c) Tidal
d) Lacustrine
Ans :
BASED ON ENVIRONMENT
Tidal : Herringbone,
Sub-tidal : Double mud drapes
Inter-tidal : Rain print, Mud crack, Adhesion ripple
Storm : Hummocky cross
Fluvial : Epsilon cross stratification, Lateral acretionary ridges
CONTINENTAL SEDIMENTARY ENVIRONMENTS
ALLUVIAL FANS : Cross bedding or graded bedding
FLUVIAL : Asymmetrical ripples, trough cross bedding, Epsilon cross bedding , Lateral accretionary surfaces (occur in point bar), Tabular CS
LACUSTRINE :
DESERT : Reverse graded, Cross bedding, Barchans
TRANSITIONAL SEDIMENTARY ENVIRONMENTS
DELTA : Cross bedding, Graded Bedding
BARRIER BEACH : Cross-bedding, symmetrical ripples, Planar lamination
LAGOON : Laminations, ripples, cross-bedding
TIDAL FLATS : Laminations, mud cracks, ripples, cross bedding
MARINE SEDIMENTARY ENVIRONMENTS
REEF :
CONTINENTAL SHELF : Laminations, cross-bedding
CONTINENTAL SLOPE : Graded bedding, cross-bedding, Laminations, flute marks, tool marks (turbidites), Hummocky CS (storm) , Herringbone CS (tidal)
ABYSSAL PLAINS : Laminations
24) Which of the following is sub-dendritic pattern?
Ans : A sub-dendritic pattern is a variation of the dendritic drainage pattern, where streams follow a branching, tree-like structure but show slight structural control due to geological variations. It typically occurs in regions where the bedrock has weak structural influences, such as gently folded or fractured rock formations.
25) The host rock of Uranium deposit of Tummalapalle is
a) Quartz-Pebble-Conglomerate
b) Sandstone
c) Dolostone
d) Granite
Ans : The Tummalapalle uranium deposit, located in Andhra Pradesh, India, is one of the largest uranium reserves in the country. The host rock for uranium mineralization in this region is dolostone, a sedimentary carbonate rock primarily composed of dolomite (CaMg(CO₃)₂).
26) The derivative of x2 sinx
a) 2xsinx - x2 cosx
b) 2xsinx - cosx
c) x2cosx - 2xsinx
d) 2x 2sinx - x2 cosx
Ans :
27) When a ray is travelling from one medium to another medium is incident at critical angle, then
a) It is reflected back to the first medium
b) Moves parallel to the surface of first medium along the interface
c) Gets refracted to the second medium
d) None of the above
Ans :
28) The magnetometer which measures value in femto units is
a) Proton precision magnetometer
b) Fluxgate magnetometer
c) Super conducting interface device magnetometer
d) Optically pumped magnetometer
Ans :
The Superconducting Quantum Interference Device (SQUID) magnetometer is an extremely sensitive magnetometer capable of detecting magnetic fields in the femtoTesla (fT) range (1 fT = 10−15 T). It works on the principles of superconductivity and quantum interference.
29)
Ans : The given image shows a spherical microfossil with multiple perforations (pores), internal shells, and spines, which is characteristic of Radiolaria.
30) The dam in which force acts towards the abutment is known as
a) Gravity dam
b) Arch dam
c) Buttress dam
d) Embankment dam
31) Which of the following mineral having high specific gravity
a) Bauxite
b) Baryte
c) Galena
d) Hematite
Ans : Galena having SG of 7.4-7.6 and hardness <3
32) The supercontinent that existed in the late Mesoproterozoic to early neoproterozoic time is _____
a) Rhodinia
b) Columbia
c) Valvaara
d) Pannotia
33) Maximum depth of investigation achieved in which array?
a) Wenner
b) Schlumberger
c) Dipole - dipole
d) Pole - pole
Ans : The maximum depth of investigation is achieved in the Pole-Pole array because it uses widely spaced current and potential electrodes, leading to deeper current penetration.
MEMORY BASED ONE LINER
1.Dip isogon divergent : Class III
2.Which mineral has six clevage : Sodalite and Sphalerite
3.Octahedron plane miller indices : 111 (8 faces)
4.Miller indices diagram qs
5.2v=90 degree diagram
6.Interference CLR related qn
7.Open cast U mine
8.Most radioactive rock : Granite
9.Old man skin : Pahoehoe lava
10.Elephant skin
11.Deccan trap word intro who : S.H sykes
12.Aperture related forams
13.Spine realated qn with diagram
14.Eh ph diagram related to iron
15.Radioactive rock
16.Dam diagram
17.Oxyatmoversion
18.Eu anomaly qn? : Positive Eu anamoly in Plagioclase
19.GroundWaterand gas pressure instrument?
20.Line joining Equal rainfall : Isohyet
21.Hill contour diagram Ash thickness ?
22.Hill around lava flow
23.Hadean .....Ttg related qn
24.The host rock of Tumalappalle Uranium : Dolostone
25.Critical angle qns anyone?
26.Antiferro magnetic minerala bears - transition metal element compund?
27.Maximum interference clr is produced when...?
28.Uranium in ground water?ppm amount
29.Increasing grade of metamorphism
30.8 fold CN with diagram
31.Volcano diagram with graph
32.Supergene sulphide enrichment
33.Phreatic zone with atmospheric pressure related qn
34.No segmented absent lophopore
35.Iron type age from old to young
36.Stratigraphy shuffle cuddaph vindyas and others
37.True thickness sum
38.Telluric current
39.Biostratigraphy related qn
40.Two fossils age to determine
41.Netslip dip slip qn
42.Double benioff zone honshu Japan
43.Chemical composition of magma based on viscosity temp ...
44.Trigonometry la oru graph sum xxdash y ydash like phi/2 -phi/2
45.One ore sum
46.Stable nucleius Odd no of pro neutron, Even no of pro neutron ?
47.Soil saturated with water during eathquake behaves plastic
48.RQD sum
49.Highest calorific value : Anthracite
50.Mean Median mode relationship
51.Tidal environ
52.Sediment-4
53.Intertidal zone range
54.Maths-3(isosceles)
55.Diagram wise volcano qs
56.Min showing internal reflection
57.Which is best viable code for unfc classification
58.Foram qs
59.Paramagnetic if become negative it s semiconductor or conductor or insulator
60.Archeological purpose which array
61.Schlumberger array diagram
62.Max vertical depth achieved in Which array
63.Water dating qs
64.Coal maceral
65.Managanese deppsit
Odd one out manganese
66.Open fold interlimb angle?
67.Ash thickness calc with conture
68.Brittle and viscous of lithosphere
69.Feather joints
70. The supercontinent that existed in the late Mesoproterizoic to early Neoproterozoic time was
71.metamorphic mineral assemble qn
72.Universal stage qn
73.variable relief in stage rotation
74.perthite microperthie
75.Lithium triangle related Argentina....
76.Iridium anomaly
77.Internal reflection ore
78.Geoid qn
79.Grouting
80.High spcG mineral
81.Soil saturated with water during eathquake behaves plastic
82.Movement of sand gravels along slope is called
83.Which stress plays minimum role in determing deformation
84.clay grain size related qn
85.Type of dam where the forces acting on the dam are transmitted onto the abutment rocks is
86.Stratigraphic equalant qn
87.which one is not used for airborne TDEMR .
88.Induced polarization qn
89.stress related qn n power 3
90.Metamorphic zone rearrange
91.stress tensor
























Comments
Post a Comment